Array & Linked list
Arrays
1. List as an array of a fixed length
In Java:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 final int [] nums = new int [4 ];x = nums[3 ]; nums[3 ] = 4 ; class Student String name; int id; } final Student[] studs = new Student[3 ];studs[1 ].name = "John" ; studs[1 ].id = 1419231 ;
In OS++(similar to c or c++):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 final nums = allocate_memory(4 *1 );x = Mem[nums + 3 ]; Mem[nums + 3 ] = 4 ; final studs = allocate_memory(3 *2 );Mem[studs + 2 *1 + 0 ] = "John" ; Mem[studs + 2 *1 + 1 ] = 1419231 ;
Linked Lists
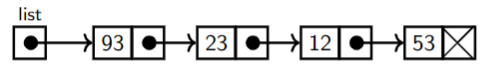
Linked list representing a list <93,23,12,53>:
1. Inserting at the beginning of a list
1 2 3 4 5 6 void insert_beg (int number) final nuewblock = allocate_memory(2 ); Mem[newblock] = number; Mem[newblock + 1 ] = Mem[list ]; Mem[list ] = newblock; }
Content for an empty list at list
2. Deleting at the beginning
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Boolean is_empty () { return (Mem[list ]==END); } void delete_beg () if is_empty{ throw EmptyListException; } final firstnode = Mem[list ]; Mem[list ] = Mem[firstnode + 1 ]; free_memory(firstnode, 2 ); }
list is the address of the list
Mem[list] stores the address of the first node.
Mem[firstnode + 1] stores the address of next node.
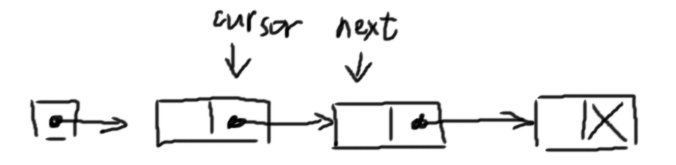
3. Look up
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 int value_at (int index) int i = 0 ; int cursor = list ; int nextnode = Mem[cursor ]; while (true ){ if (nextnode == END){ throw OutOfBoundsException; } if (i == index){ break ; } cursor = nextnode + 1 ; nextnode = Mem[cursor ]; i++; } return Mem[nextnode]; }
Return the value stored at index.
4. Insert at the end
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 void insert_end (int number) final newblock = allocate_memory(2 ); Mem[newblock] = number; Mem[newblock + 1 ] = END; int cursor = list ; while (Mem[cursor ]! = END){ cursor = Mem[cursor ] + 1 ; } Mem[cursor ] = newblock; }
5. Insert at the end (recursion)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 void insert_end (int number) insert_list(listaddress,number); } void insert_end (int listaddress, int number) final startnode = Mem[listaddress]; if (startnode == END){ final newblock = allocate_memory(2 ); Mem[newblock] = number; Mem[newblock + 1 ] = END; Mem[listaddress] = newblock; }else { insertlist(startnode + 1 , number); } }
Modifications
Linked list with a pointer to the last node
Doubly linked list.
Other
Memory model
Notation
The content stored in location at index:
Mem[<index>]
Allocate n pieces of memory:
allocate_memory(n)
Free n pieces of memory start from <address>
free_memory(address,n)